반응형
BasicAuthenticationFilter
- 기본적으로 서버에서 내려줄 수 없는 경우에 사용합니다. 최근에 SPA 기반의 개발 시 클라이언트에서 자바스크립트를 통해 로그인폼을 만들기 때문에 서버를 통해서 페이지 리다이렉션을 통해서 로그인을 하는 것이 아니기 때문에 BasicAuthentication을 사용해야 합니다.
다음과 같이 설정합니다.
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.csrf().disable()
.authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.httpBasic()
;
}
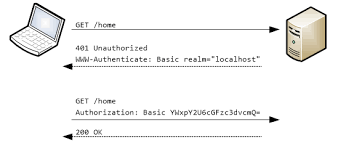
서버에 보호되는 서비스가 존재한다고 했을 때 예를 들어 GET /home 이 있다면, 해당 필터에서 SecurityContext에 인증된 토큰이 없다면 아래와 같은 포맷의 토큰을 받아서 인증처리를 하고 갑니다. 이 SecurityContext에는 인증 정보가 존재하기 때문입니다.
developer.mozilla.org/ko/docs/Web/HTTP/Authentication
HTTP 인증 - HTTP | MDN
HTTP 인증 HTTP는 액세스 제어와 인증을 위한 프레임워크를 제공합니다. 가장 일반적인 인증 방식은 "Basic" 인증 방식입니다. 이 페이지에서는 일반적인 HTTP 인증 프레임워크를 소개하고 서버에 HT
developer.mozilla.org
- http에서는 header에 username:password 값이 묻어서 가기 때문에 보안에 매우 취약합니다. 그래서, 반드시 https 프로토콜에서 사용할 것을 권장하고 있습니다. 사실이건 base64 인코딩이기 때문에 복호화가 간단하기 때문입니다.
- 최초 로그인 시에만 인증을 처리하고, 이후에는 session에 의존합니다. 또 RememberMe 를 설정한 경우, remember-me 쿠키가 브라우저에 저장되기 때문에 세션이 만료된 이후라도 브라우저 기반의 앱에서는 장시간 서비스를 로그인 페이지를 거치지 않고 이용할 수 있습니다.
- 에러가 나면 401 (UnAuthorized) 에러를 내려보냅니다.
SecurityContextPersistenceFilter
- SecurityContext를 저장하고 있는 저장소에서 만료되지 않은 인증이 있으면 SecurityContextHolder에 넣어줍니다. 이전에는 HttpSessionContextIntegrationFilter 이란 필터가 있었는데, 저장소가 반드시 세션일 필요는 없기 때문에 추상화된 객체로 발전된 필터라고 볼 수 있습니다.
- HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository : 서버 세션에 SecurityContext 를 저장하는 기본 저장소.
Bearer 토큰
인증받은 세션 아이디나, 인증된 토큰을 헤더에 실어서 보내는 것이 Bearer토큰입니다.
최초 로그인하고 유저를 인증하면은 유저에 대한 최소한의 정보를 남겨놓고 그 값을 사용해 해당 토큰으로 서버와 통신을 하는 것입니다.
- JWT 토큰
- Opaque 토큰
연습
Security Config
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth
.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser(
User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder()
.username("user1")
.password("1111")
.roles("USER")
.build()
);
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//post방식은 기본적으로 csrf필터가 작동함
http
.csrf().disable()
.authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.httpBasic()
;
}
}
Controller
@RestController
public class HomeController {
@GetMapping("/greeting")
public String greeting(){
return "hello";
}
@PostMapping("/greeting")
public String greeting(@RequestBody String name) {
return "hello " + name;
}
}
test
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
class BasicAuthenticationTestApplicationTest {
@LocalServerPort
int port;
private String greetingUrl() {
return "http://localhost:" + port + "/greeting";
}
RestTemplate client = new RestTemplate();
@DisplayName("1. 인증실패")
@Test
void test_1() {
HttpClientErrorException exception = assertThrows(HttpClientErrorException.class, () -> {
client.getForObject(greetingUrl(), String.class);
});
assertEquals(401, exception.getRawStatusCode());
}
@DisplayName("2. 인증성공")
@Test
void test_2() {
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.add(HttpHeaders.AUTHORIZATION,"Basic "+ Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(
"user1:1111".getBytes()
));
HttpEntity entity = new HttpEntity(null,headers);
ResponseEntity response = client.exchange(greetingUrl(), HttpMethod.GET, entity, String.class);
assertEquals("hello", response.getBody());
System.out.println(response.getBody());
}
@DisplayName("3. 인증성공2")
@Test
void test_3() {
//기본적으로 Basic Token을 지원함
TestRestTemplate testClient = new TestRestTemplate("user1", "1111");
String response = testClient.getForObject(greetingUrl(), String.class);
assertEquals("hello", response);
}
@DisplayName("3. Post 인증")
@Test
void test_4() {
//기본적으로 Basic Token을 지원함
TestRestTemplate testClient = new TestRestTemplate("user1", "1111");
String response = testClient.postForObject(greetingUrl(), "sung",String.class);
assertEquals("hello sung", response);
}
}
반응형
'Spring|Spring-boot > Spring Security' 카테고리의 다른 글
| SecurityContextPersistenceFilter (0) | 2022.10.30 |
|---|---|
| Spring Security(4) (0) | 2021.04.04 |
| Spring Security Form Login (0) | 2021.03.28 |
| Spring Security(2) (0) | 2021.03.21 |
| Spring Security(1) (0) | 2021.03.21 |



댓글